Ear infections are one of the most common ENT problems affecting both children and adults. They occur when bacteria or viruses infect the middle or outer ear, often following a cold, sinus infection, or throat infection. If not treated on time, ear infections can cause severe pain, fever, discharge from the ear, and even temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Common symptoms of ear infections include ear pain, a feeling of fullness in the ear, reduced hearing, ringing sensation, dizziness, and fluid drainage. In children, symptoms may also include irritability, crying, difficulty sleeping, or pulling at the ear. Early diagnosis by an ENT specialist is essential to prevent complications.
There are different types of ear infections such as outer ear infection (otitis externa), middle ear infection (otitis media), and inner ear infections. Each type requires a specific treatment approach. An ENT doctor uses ear examination tools and hearing tests to accurately identify the type and severity of the infection.
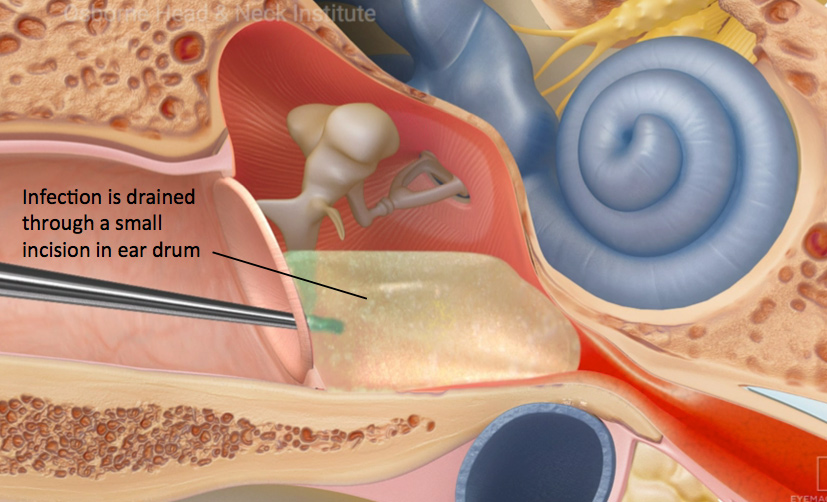
Treatment for ear infections depends on the cause and severity. Mild infections may be treated with medications such as antibiotics, ear drops, pain relievers, and anti-inflammatory drugs. In chronic or severe cases, procedures like ear suction cleaning or minor surgical intervention may be required to restore proper ear function.
Timely ENT treatment ensures fast relief from pain, prevents hearing damage, and promotes complete recovery. Maintaining ear hygiene, avoiding self-medication, and consulting an ENT specialist at the first sign of symptoms can greatly reduce the risk of recurring ear infections and long-term complications.